Everyone wants their site to rank the best it possibly can in search engines.
Bloggers leverage SEO tools and webmaster tools, write high-quality unique content, and focus on building effective internal links to improve their SEO. Yet, duplicate content issues can still rear their ugly head to hurt website rankings.
I frequently audit our website as part of the steps we take to increase our website traffic. More often than not, I find at least one issue with duplicate content.

Get personalized content recommendations and answers drawn from our website. Simply type your question or topic of interest, and our AI assistant will help you find relevant articles, tips, and insights. You can also have a natural conversation to explore topics in more depth.
What is Duplicate Content?
Duplicate content is much more than just posting identical content on your website. Issues range from similar content on multiple webpages to structural issues with your HTML. Duplicate content typically refers to significant blocks of similar content on multiple webpages or spread across multiple domains.
Search engines have pushed back hard against websites containing duplicate content. Depending on how the site is created, multiple pages with the same content can seem really spammy and create a poor user experience.
Not only have you created a poor experience for your human visitors, but it’s also a poor experience for search engines—especially since search engines don’t want to serve duplicate results for a search query.
Duplicate content issues at scale tend to significantly hurt your rankings, but don’t worry, a few paragraphs of content or duplicate pages won’t crash your rankings or prompt Google to penalize your site.
In some cases, duplicate content is deceptive in origin in an attempt to manipulate search engine rankings. If you create deceptive duplicate content, you risk having your site removed from Google.
Google’s official policy on duplicate content is this:
In the rare cases in which Google perceives that duplicate content may be shown with intent to manipulate our rankings and deceive our users, we’ll also make appropriate adjustments in the indexing and ranking of the sites involved. As a result, the ranking of the site may suffer, or the site might be removed entirely from the Google index, in which case it will no longer appear in search results.
If you are deliberately creating duplicate content, we can’t help you.
More often than not, issues are not deceptive in origin, and the tips in this article can help you identify and correct issues.
Content-Based Duplicate Content Issues
These issues arise because you use the same words over and over again on your site. They also crop up from issues like keyword stuffing or repeating blocks of content.
To avoid perpetrating duplicate content yourself, do not duplicate substantive blocks of content either within your site or across domains. This includes exact as well as considerably similar matches. The topics below highlight the most common sources of content-based issues.
Product Pages
Think of an ecommerce site where the products are mainly the same but with a slight variation (e.g. same shoes in 6 different colors), the product descriptions are likely going to be exactly the same if not very similar for all those variations. Instead of separate pages for each variation or color, use a plugin with this functionality built-in (like WooCommerce).
For example, on Ohmm Scrubs we want to show all the possible size and color options for each article of clothing. Product variations allow us to do this so the shopping experience is streamlined and there is no risk of duplicate content.
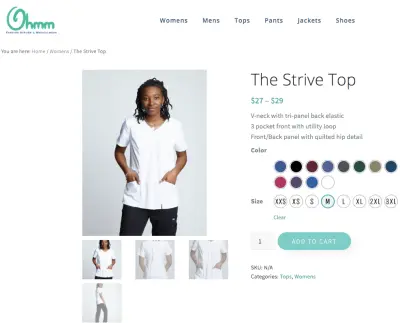
When you absolutely need individual pages for similar products, either find a way to differentiate the content on the page or use a canonical tag to point to an optimized category archive page.
Landing Pages
When marketing on your website, you may need to create multiple similar landing pages for PPC ads, A/B testing, or other marketing purposes. Noindex these pages to avoid duplicate content issues and to avoid those pages competing with other core pages on your site.
The purpose of indexing a page is to make it available to searchers via organic search traffic. These types of landing pages don’t need to be indexed because often they are temporary, and they are not intended to be found organically. They are intended for direct traffic only. (In other words, you are providing the link to your audience; they are not searching for it.)
Content Theft and “Scrapers”
If your content is remarkable (as it should be!) then others may try to steal it to generate clicks to their own site. These people or bots are often called “content scrapers.”
Content scraping can be done with a basic copy/paste or by bots that can crawl sites and copy multiple pages. Bloggers and other regular content publishers are usually targeted by scrapers to get new content for their sites and steal traffic from the original publisher.
If this happens, you can request that the site remove your content by filing a request through the Digital Millennium Copyright Act. Unfortunately, this is a long and complicated process that doesn’t guarantee action against the scraper.
The good news is that Googlebot and other crawlers are pretty good at deciphering the original source of content. One indicator is which piece of content was indexed first. The first to get indexed is usually the original source and Google will recognize it as such.
Freelance Writers
You should closely monitor any outside or freelance writers you hire to make sure you purchase 100% original content. Some writers sell the same content to multiple sites. This doesn’t necessarily mean they are trying to scam you; they may not be aware what they are doing can be damaging to the businesses they are selling to.
You should establish clear guidelines with your writers that they must provide original content, and if they are referencing other sources then proper citations should be included. Also, be sure to run the content through a plagiarism checker.
Quotes are fine as long as you source them properly within the post and include a reference section at the end. If your post is over 50% similar to another page then that’s considered plagiarism, and you shouldn’t publish that content.
Always strive for as much originality as possible; your unique expertise is what sets you apart from your competition.
Guest Posts
Your site may also have guest posts, or you may do guesting posting on other blogs. Often in the case of guest posts, the writer either already has posted the content on their own site or they plan to.
Use rel=canonical to point to the original article. The purpose of guest-posting is more about gaining exposure to new audiences (less to do with getting on search engine results pages), so it shouldn’t be a huge concern that your post may not be shown as the original source.
That being said, it is a nice gesture to link back to the author or their site. The better the relationships you can form with your fellow bloggers, the more likely you’ll get backlinks from them too at some point.
Technical-Based Duplicate Content Issues
There are a few technical issues that can cause duplicate content issues and cause your search engine rankings to drop.
Two of the most common are improperly configuring your preferred domain when adding SSL or changing from www to non-www domain prefixes and elements such as title tags, H1 tags, URL slugs, and meta descriptions.
These issues may also creep up because of poorly developed WordPress themes or result from tools or features that you added to your website that may not be configured properly.
Here’s an example of a few types of technical duplicate content issues that can result from adding features or functionality to your site and not setting the configurations correctly.
Find & Fix Content-Based Duplicate Content
It’s good site maintenance to run a website audit periodically and check for duplicate content problems or other technical SEO issues.
While some people like Siteliner because it’s a fast and free tool, it has some limitations. Namely, it will only scan 250 pages. It also limits you to one scan per site per month. The biggest problem is that it just not give the level detail you really need to properly audit your site, especially if you have a large blog.
After you’ve scanned your site and found some duplicate content, now you need to do something about it.
When to Use Canonical Links
Designate a canonical URL to tell Google what URL the “duplicate” page should point to. (This is simple to do if you use Yoast. See the advanced settings when you are in the post editor.)
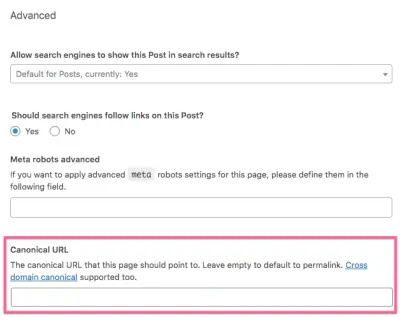
Use canonical links to consolidate duplicate URLs by defining a canonical page for your content that spans multiple platforms (a desktop and a mobile URL). You should also consolidate if you have an SSL certificate with HTTPS on most of your pages but some could still be HTTP.
Example of these duplicate URLs look like this:
- website.com/post-title
- website.com/category/post-title
Your canonical URL is what Google marks as the most representative page for that content and all traffic is directed there.
When to Combine & 301 Redirect
Combine duplicate content and use a 301 redirect when there is no need to keep all the pages. Do this for thin content pages or those that have no real value.
Additionally, if your blog has existed for multiple years, there’s a possibility that you have created multiple related blog posts. While not exactly “duplicate content,” these closely related posts might be better served by combining them into a single well-written post. Look for this type of content and make sure to account for reviewing it when developing your content marketing plan and SEO strategy. This also allows you to breathe new life into old posts and get more traffic out of them.
Find & Fix Technical-based Duplicate Content
The topics listed above in technical-based duplicate content are a bit harder to fix and would typically require your theme developer to fix. We’re super excited to keep an SEO focus on Mai Theme and recently announced the merger of SEO Themes into Mai Theme.
The Bottom Line
Duplicate content is an issue for pretty much every website out there. It’s something you will always have to keep a close eye on, but it is manageable. If you take steps to clean up and prevent duplicate content you’ll see the benefits with better SEO and higher traffic in no time!
Download the How to Start Blogging Guide
Explore this FREE GUIDE to take a deep dive into how to start blogging to make money. Get a PDF version of this guide right to your email, plus weekly tips from our blogging experts at BizBudding.







